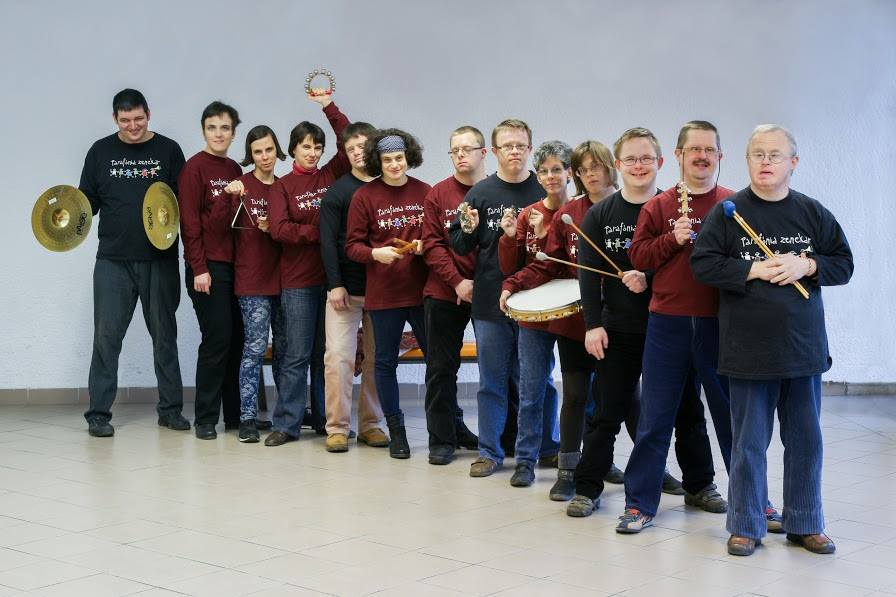
In this subpage you will find a variety of inspiring initiatives that treat people with mental disadvantages to improve their wellbeing and uncover their hidden talents. The following organisations and projects address different health issues ranging from autism to brain injuries.
The Ronnie Gardiner Method
The Ronnie Gardiner Method (RGM) is a novel rhythm- and music-based rehabilitation method that has been used within Swedish healthcare and rehabilitation since 1993, with international dissemination since 2009. RGM is a structured, multimodal and multi-sensory exercise method which combines movement and cognitive challenge in a playful way in order to improve cognitive functions like concentration, coordination, and memory. It also enhances postural control, energy, motivation and lifts the mood. The RGM is built on the scientific principles of motor control, motor learning, postural control, and neuroplasticity, including new ideas of enriched environment. The method is used to address many conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, MS, stroke, acquired brain injury, children with reading and learning difficulties and also as an activity to enhance healthy aging.
It has now passed 35 years since the birth of the method. It was in 1980 that a personal tragedy was to transform Ronnie’s life and seriously awaken his interest in the workings of the brain and its functions. With his knowledge of playing the drums he began to develop a form of training with the object to stimulate the brain as much as possible.
Chiltern Music Therapy
Whereas some providers only offer one type of approach, the Chiltern Music Therapy team has a thorough understanding of psychodynamic, medical, behavioural and person centred approaches.
The team contains a wealth of knowledge and experience in highly specialist areas covering the complete lifecycle from Acute Neonatal through to end of life care. Their children’s and adult services extend from one-to-one care in homes or in-patient settings , through to community groups and schools ensuring that they can provide the best possible provision in the right setting for each individual client. That includes also weekly or biweekly get-togethers for disabled people, where they can sing, make music together and through that develop social skills as it is a great place for social interaction.
The British Academy of Sound Therapy
The British Academy of Sound Therapy provide courses that teach people how to use sound in their community to improve health and well-being. Their aim is to give their students the knowledge and skills to be able to develop professional and safe businesses using tried and tested techniques. Their vision is to continue to raise awareness of this important field with training courses, projects, events and a growing range of products.
Punk Therapy
In a 5-part programme called “Punk Therapy”, a TV show that follows nine young people with different mental disadvantages who started dreaming about making a band. It was inspired by the success story of the Finnish ensemble Pertti Kurikkaan Nimipäivät. The band’s mentor was the flagship of the Estonian folk-metal music “Metsatöll”. The TV programme shows the path from the very beginning to the real concert on stage.
The Programme was made by Kaidor Kahar.
Click on the photo and you’ll see the video about the program.
Guided Imagery and Music
Guided Imagery and Music (GIM) is a music psychotherapeutic method in which the patient hears a selection of mostly classical music in a relaxed state and communicates his experience (= imaginations) to the therapist. Theoretical background, clinical application, as well as method-specific understanding of music and imagination theory of GIM and its modifications – these areas are covered in this textbook. The authors give a detailed and comprehensive insight into the method, both for psychotherapeutic and medical professionals, and for GIM training candidates.
The ULWILA Method
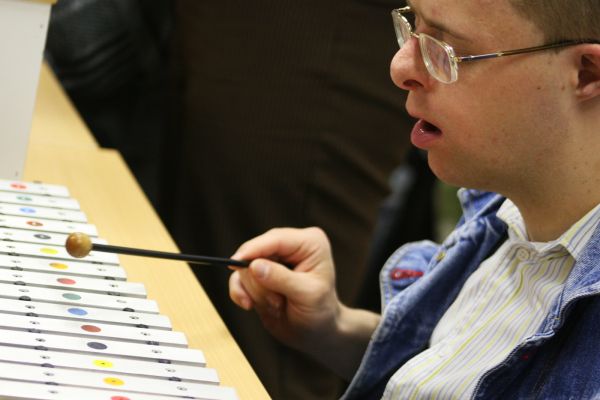
The key concept of the ULWILA method is based on the fact that the inability to read normal sheet music served as the greatest impediment for individuals struggling with intellectual challenges to make music collectively. Ullrich became the father of a new method of reading music with the help of a color scheme that replaces the 5 bar line system. The method was adapted to Hungary by Anna Vető in 1991.
Each tone of the diatonic scale has a different color. These colours, which appear in the score, are also indicated beside the strings, pipes and keys of the instruments. According to Ullrich’s method, the children can match a tone with its corresponding colour without even knowing the names of the colors (Ullrich & Vető 1996).
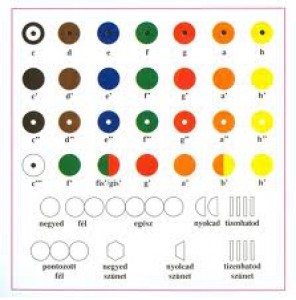
The semitone is simply denoted by the two colours, which the tone is between.
The marking of the rhythm is also simple: The quarter note is a full circle, a half note is two circles interlinked, the whole note consists of four circles and an eighth note is a semicircle. The musical rest is marked by a blank hexagon. Further rhythm values denoted according to the above rules.
Instead of barlines the notation use signs for the strong beat.
It is also important to mention that the method uses only the colors that can be find in nature. The method uses dark colours for lower and light for the upper tones. Therefore, the visual manifestation of the notation supports musical understanding. Skilled players after years of learning are able to play from a partiture.
One of the most important characteristics of this method is that it teaches music in groups. This is different from the western tradition of instrumental music education which is based on a method of instruction where musicians gain experience through individual lessons.
The orchestra playing with this method and whose founder was Anna Vető in 1997 is the Paraphony orchestra. The association, whose umbrella this orchestra is under is the “Music Belongs to Everyone” Association.
Talent and being mentally challenged
“Talent and being mentally challenged” is an essay written in Hungarian by Dr. Katalin Gruiz, president of the Down Syndrome Foundation.
Relationship matters
NORCE is a new and forward-looking research institute, with expertise in a wide range of fields and strong communities of knowledge. Their solutions address key challenges for society and contribute to value creation on the local, national and global levels.
In this study they have examined how the relational factors in music therapy can contribute to a positive outcome of therapy for children with autism.
Improvisational Music Therapy
The TIME-A Project is a project measuring the impact of improvisational music on autistic children. The main results, published in JAMA in August 2017, indicated that improvisational music therapy did not reduce autism symptoms more than enhanced standard care. However, positive effects of music therapy were found in subscales and additional post-hoc analyses.
Furthermore, music therapy was well accepted by parents, children, and staff; parents reported their children’s enjoyment and benefit from improvisational music therapy; and parents reported their own involvement in music therapy as positive.
Aphasia
Aphasia is the name given to a collection of language disorders caused by damage to the brain. A requirement for a diagnosis of aphasia is that, prior to the illness or injury, the person‘s language skills were normal. The difficulties of people with aphasia can range from occasional trouble ending words to losing the ability to speak, read, or write, but does not affect intelligence. The term „aphasia“ implies a problem with one or more functions that are essential and specific to language function. Aphasia is most commonly caused by stroke. It can also be caused by other brain diseases, including cancer (brain tumour), epilepsy, and Alzheimer‘s disease, or by a head injury.
Aphasia Choir in Hungary lead by Zsófia Fekete has made great experienced with teaching how to speak again through music.
Brain Injury Matters
Brain Injury Matters was established in 1999 to support adults and families affected by acquired brain injury after discharge from statutory rehabilitation services. Today they offer a range of supports to children, adults and families across Northern Ireland to enable them live the life they choose.
They offer day service three times a week which includes art, drama, music therapy, peer support groups, exercise classes, yoga and IT Support. They also offer counselling, neuro-physiotherapy, befriending service and a community outreach service.
Social Inclusion through Theatre
Social inclusion through arts in the theatre Baltazár Színház (HU). The only theater in Hungary, that employs and pays only mentally challenged actors, most of them with Down Syndrome. They provide free schooling for their disadvantaged actors, this meaning singing classes, acting classes throughout the day. This way these actors are able to lead a mostly normal lifestyle, like any of us healthy people do, they are able to make friends, have school mates, are facing hardships at tests, but can enjoy gratifying their passion on stage as well.
Social Theatre
Social Theatre™ is a program that utilises improvisation, sketch comedy and collaborative writing to teach social skills in real time. Though not directly connected to music it still provides a lot of free material for you to use. One of the most important components is learning how to work through a group process of collaborative writing in which brainstorming, evaluating and practising help turn ideas into plays. The plays incorporate social messages about how to turn social awkwardness into social success, how to deal with bullies and being accepted. When writing about social awkwardness, participants learn how to laugh at past experiences and just being human. … read further














